DNS Server: A Key Element of the Internet
DNS server: what is it?
The Internet is a network consisting of billions of devices, smartphones, servers, laptops, tablets and desktop computers, routers that are in constant communication. The ability to accurately and quickly exchange data is ensured by the presence of a personal IP address for each device, which can be compared either with a postal address or a phone number.

An IP address is needed not only for devices, but also for websites. Its classic spelling, several groups of numbers, letters separated by dots, colons, hyphens, however, is difficult to remember, which is inconvenient for users. The domain name system, DNS, is designed to solve this problem, assigning a specific letter name to each digital combination, which is easier to write and remember. The basis of this system is DNS servers. What are their features? What functions do they perform?
General concept
The DNS system can be compared to a telephone directory. Several decades ago, you had to open this book to find the desired phone number by the subscriber's name or the name of the organization. The necessary records are also stored on the system's servers. The user does not need to specify a specific number in the address bar, the name of the site is enough, the transformations necessary for the transition will be performed automatically.
For fun, the user can enter the exact IP address corresponding to the site in the line. In this case, it will also open without problems, but keeping dozens of digital combinations in memory is inconvenient, and often impossible. With names, everything is much simpler and clearer.

DNS servers are the most important links in the domain name system, used to store data about website addresses, the number of which is in the hundreds of millions and billions. In addition to storage, they also perform some other tasks that require a more detailed analysis.
The DNS system is characterized by the following:
- Distribution of data management and storage. Each part is serviced by a specific enterprise, server.
- Data caching. Temporary storage of information helps reduce the load on the system.
- Backup. Several DNS servers have access to the same data, which eliminates loss, the inability to interact if one of them fails, and ensures stable operation of the entire system.
Main functions
DNS servers not only store, but also cache information. The caching algorithm increases the overall speed of DNS and helps distribute the load evenly. The capacity of servers is not unlimited, and therefore storing all data in one place is an impossible task. When a user tries to open a specific site, the system will first conduct a local check, examine the “hosts” file located on the computer, and try to find the necessary data there. If the result is negative, the request is transferred to a higher level, the local DNS server serviced by the provider.

A local DNS server usually exchanges data with other local resources where the site is located. After finding the required information, the user's browser opens the required pages. The found data is stored on local servers, which eliminates the need to search for and download it again during subsequent attempts to open it. This process is called caching.
Working algorithm
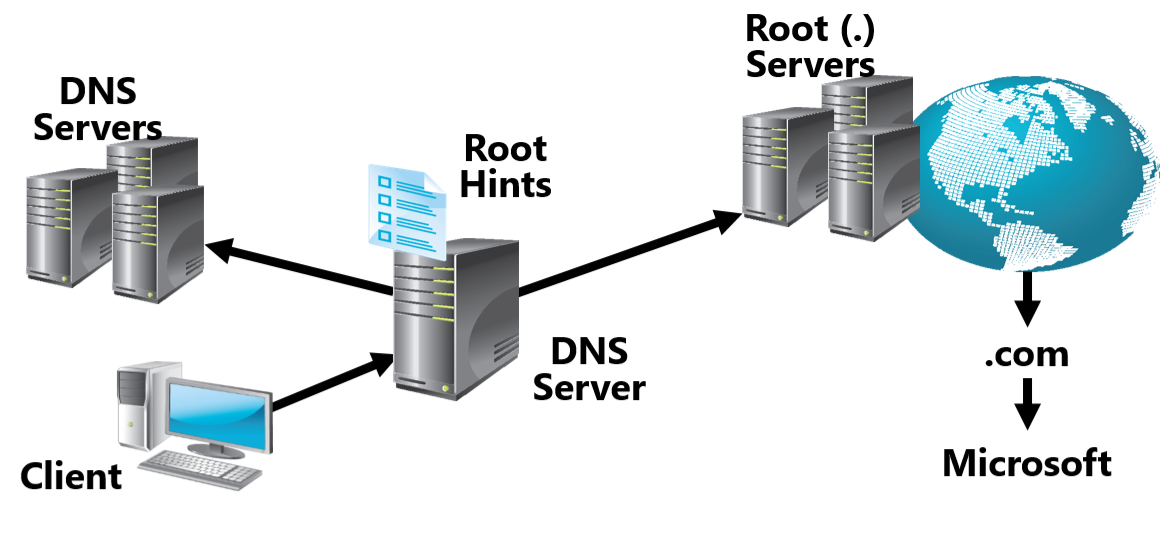
The scheme of functioning of the domain name system can be presented as follows:
- Receiving a user request by the browser. This request is sent to the network server, whose task is to find the IP address corresponding to the domain name. If an answer is found, the page is immediately opened, otherwise the search begins at higher or root levels.
- The root server redirects the request to the first level, the second and further, until a match is found between the domain name and IP address.
- Displaying the searched page in the browser.
Classification
The DNS system is based on servers of various categories. If the data on the site being searched for is not found in the “hosts” file, then the DNS resolver, a local-level resource, comes into play. As a rule, it is not even a full-fledged large-scale server, but a computer on the Internet provider’s side. The resolver processes the name of the site needed by the user and accesses its own database. If there is a match, a response is sent, the page opens, and the search stops. If the resolver is powerless, the following DNS servers come into play:
- Root. In English literature - root. There are only 13 of them in the world, however, they are very large-scale, have enormous performance, and can handle millions of requests per second. The root DNS server does not disclose the required IP address when accessing it; its task is to determine the route for further transmission of the request, which allows you to obtain the required data.
- Top level. They are also TLDs. The root DNS servers provide information about which TLD to contact to clarify the addresses of domain names. Each server of this level is assigned its own “area of responsibility” corresponding to the domain. It is interesting that the TLD does not provide information about a specific IP; it also redirects to servers that perform authoritative functions.
- Authoritative. It is on these servers that information about the correspondence of IP addresses to certain domain names is stored. Accordingly, they provide the resolver with the required data, help open the desired page on the user's computer.
The DNS structure looks quite cumbersome, including many servers and devices, however, its operation, despite the apparent complexity, is optimized as much as possible. Interaction between hardware components takes several thousandths of a second.
Geography of root DNS servers
The number of root DNS servers is 13, however, to ensure the stability of the domain name system, its security, and resilience to failures, they have many copies, taking into account which the number is 123. The geography of their distribution is as follows:
- 40 - USA and Canada;
- 35 - European countries;
- 6 - South American countries;
- 3 - African countries;
- 39 - the rest of the world.
This placement is not accidental, it corresponds to the number of active Internet users and, accordingly, the volume of requests. 5 copies of root DNS servers also function in the Russian Federation, they are located in the largest cities, Moscow, St. Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg and Rostov-on-Don.
Settings and records
To ensure the correct operation of the DNS server, it must be configured correctly, and the necessary records must be entered. This is necessary because one domain name is often associated with different addresses, for example, the main site, its mail server and numerous subdomains.
The data that assigns a domain name to a specific address is stored on the server, in a special file. This file should be edited, and records should be added to it as needed. The list of main records looks like this:
- A – IP address of the network resource corresponding to a specific domain name.
- MX – IP address associated with the mail server.
- CNAME – is needed to indicate the relationship between identical domain names, in most cases – to associate subdomains.
- NS – indicates the location of DNS servers storing other resource records.
- TXT – contains any necessary text data related to the domain.
- SPF – contains information about servers that can handle mailings on behalf of the designated domain.
- SOA – a record with basic data about the server.
On the issue of security
The security of root servers is an extremely important point, the stability of the entire domain name system depends on their performance. One of the largest attacks was registered in the fall of 2002. Hackers managed to block the work of 10 out of 13 root servers. Such activity is still encountered today, which causes failures in the World Wide Web, does not allow access to some sites, primarily social networks.

However, security technologies have made great strides since 2002, so it is possible to do without serious consequences. The following methods are most widely used:
- uRPF. It is based on a check to determine whether the device can receive a data packet from a specific recipient. If the result is negative, the transmission is blocked. The method is quite effective, but does not provide absolute protection against fake traffic.
- IP Source Guard. Development of the previous method. Algorithms monitor traffic, determine IP addresses of network equipment, and form information transfer tables. If a previously verified source suddenly starts using a different address, the packets are rejected.
- DNS-Validator. A special application that controls data transfer within the DNS system, comparing requests and responses. If discrepancies are detected, the exchange of information is blocked, or the user receives a warning notification, depending on the settings.
Summing Up
The DNS domain name system is the main guide through the global network, without which browsers and users would simply not be able to get to the necessary sites and pages. DNS servers are the most important components of this system, where the data necessary for correct operation is stored.
The appearance of DNS dates back to the 80s of the last century, however, it continues to actively develop and modernize, which allows it to meet the requirements of the time, network security, and correctly serve a steadily increasing number of users.
Answers to popular questions
How soon can I start using the service?
The user account is opened immediately after the application is submitted.
Immediately after making the payment, you can start using the service immediately.